Identify the Structures of the Hindbrain and Describe Their Functions
It consists of the medulla oblongata. It contains the cerebral cortex which is the outermost layer of the brain and what is responsible for information processing.

Hindbrain Definition Function Structures Diagram Location Facts Britannica
Centres for control of many vital functions monitoring.
. The largest part of the forebrain is the cerebrum. The hindbrain is composed of the brainstem and the cerebellum and each structure is responsible for certain functions. This hindbrain structure aids in fine movement coordination balance and equilibrium maintenance and muscle tone.
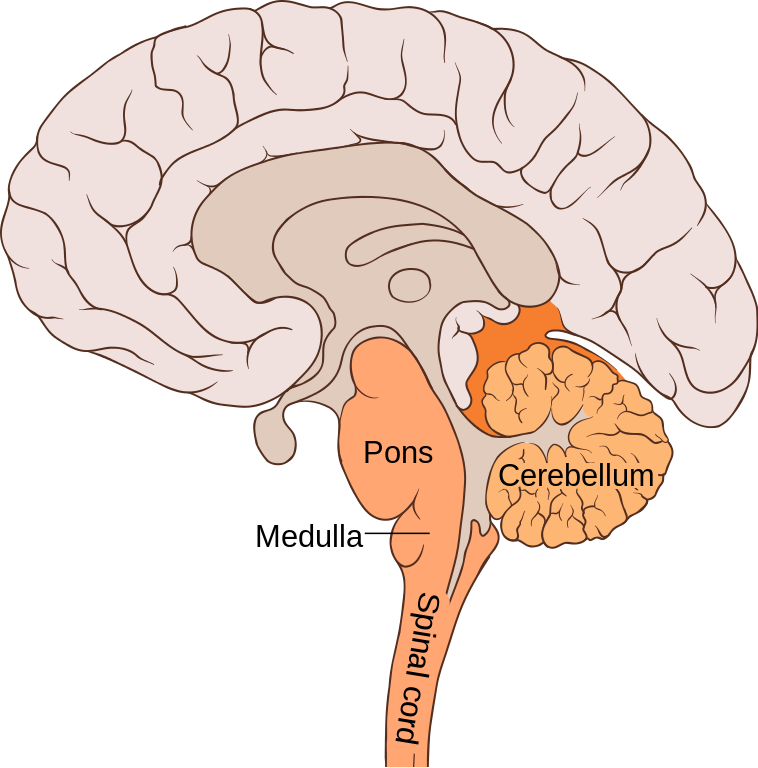
As mentioned the hindbrain is comprised of the pons medulla and cerebellar structures of your brain which together essentially act as the commander in charge of your automated systems talk. Identify the basic regions of the hindbrain and describe their functions. The hindbrain contains several structures that regulate autonomic functions which are essential to survival and not under our conscious control.
The medulla lies next to the spinal cord and controls functions outside conscious control such as breathing and blood flow. Forebrain Midbrain and Hindbrain. In other words the medulla controls essential functions.
Each of these structures is described below. The medulla is largely responsible for unconscious biological functions such as breathing heart and blood vessel activity swallowing vomiting sneezing and coughing. IDENTIFY AND DESCRIBE THE STRUCTURES AND THEIR CORRESPONDING FUNCTIONS LOCATED IN THE FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN AND HINDBRAIN-Forebrain-Thalamus - relay station from the sensory organs.
The midbrain consists of various cranial nerve nuclei tectum tegmentum colliculi and crura Celebi. The forebrain includes the cortex basal ganglia and the limbic system. The myelencephalon is the lower region of the hindbrain located below the metencephalon and above the spinal cord.
Brainly UserBrainly User. The main function of this human brain structure is to control certain visceral functions in body including heart rate breathing and blood pressure. Brain Stem consists of.
This brain structure relays motor and sensory signals between the. The three primary divisions are the forebrain the midbrain and the hindbrain. Hindbrain Control Center for Visceral Functions.
It is divided into left and right hemispheres. The hindbrain is composed of the medulla the pons and the cerebellum. Regulates sleep wakefulness and levels of arousal.
The medulla is located at the top of the spinal column. The hindbrain coordinates functions that are fundamental to survival including respiratory rhythm motor activity sleep and. Hindbrain Medulla Oblongata - Al nerve fibres ascending and descending between the brain and spinal cord pass through the medulla.
The brainstem at the top of the spinal cord controls breathing the beating of the heart and the diameter of blood vessels. The hindbrain can be further divided into 3 parts. Extension of the spinal cord into the school that coordinates heart rate and circulation in respiration.
The forebrain midbrain and hindbrain structure the three major parts of the brain. The medulla oblongata sits at the transition zone between the brain and the spinal cord. Hindbrain also called rhombencephalon region of the developing vertebrate brain that is composed of the medulla oblongata the pons and the cerebellum.
Signals for many functions enter and leave medulla by way of spinal cord and 4 pairs of cranial nerves IX X XI and XII. A structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. The three structures of the hindbrain are the medulla pons and cerebellum.
In other words the medulla. Large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills. The hindbrain is composed of the medulla the pons and the cerebellum.
The hindbrain includes the medulla pons and cerebellum. The medulla lies next to the spinal cord and controls functions outside conscious control such as breathing and blood flow. 4 Identify the structures that form part of the Hindbrain The hindbrain the from HPS 310 at Deakin University.
The forebrain structures include the cerebrum thalamus hypothalamus pituitary gland limbic system and olfactory bulb. Medulla oblongata pons and cerebellum. Most caudal part of the brain.
Breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing. Sleep respiration swallowing bladder control hearing equilibrium taste and. Main source of input to the cortex-Hypothalamus - small area near the face which conveys messages to the pituitary gland to alter the release of.
The hindbrain which includes the medulla oblongata the pons and the cerebellum is responsible some of the oldest and most primitive body functions. The midbrain is important for both sensory and motor functions.

Hindbrain Parts Function And Location Simply Psychology

Hindbrain Parts Function And Location Simply Psychology

The Hindbrain Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
No comments for "Identify the Structures of the Hindbrain and Describe Their Functions"
Post a Comment